A. General Information
Exchange electronic phytosanitary certificates (ePhytos) between Korea and the USA
B. Lessons Learned
The Republic of Korea and the USA started a digital operation to adopt the ePhyto solution developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC). It allows for the exchange of electronic phytosanitary certificates.
The Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (APQA) of the Republic of Korea started a new digital operation to exchange electronic phytosanitary certificates (ePhytos) developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC). The Republic of Korea will replace paper phytosanitary certificates exchanged with the United States Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) with ePhytos for all plant products traded with the United States of America.
When importers apply phytosanitary import inspection through Customs single window system, they can click “ePhyto” and put ePhyto numbers. This info is automatically transferred to APQA system which is connected to the IPPC hub to retrieve the ePhyto. If exporters want to use ePhyto, after export inspection relevant information is filled in the National system and ePhyto is transferred to the hub upon approval of the relevant senior staff.
To face the challenges deriving from the use of paper certificates (paper certificates can be costly, are logistically complicated and difficult to protect against fraud).
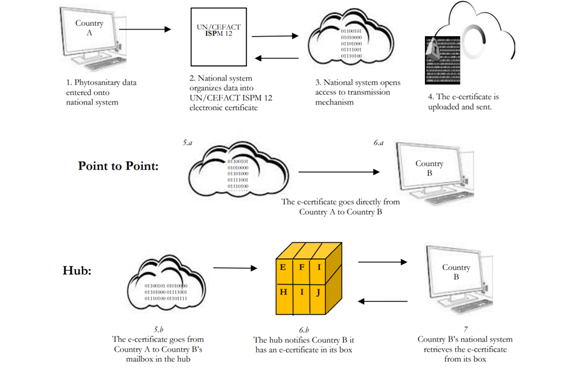
Exchange of electronic Phytosanitary Certificates
The national developed systems are used to exchange ePhyto data via the HUB (https://www.ephytoexchange.org/landing/hub/index.html)
The HUB is a centralized system to facilitate exchange of ePhytos between NPPOs with a set of prescribed rules of connection and defined structure/codes/terms for the XML message.
Use of the Hub is voluntary
The Hub is a single, multilateral system
The Hub will be available 24/7 (secure and monitored)
No information (messages, transactions) should be lost
There is a single exchange protocol
The IPPC determines the version of UN/CEFACT schema
Participating countries will require a National System to exchange ePhyto through the Hub or use the Generic system
For more detail refer to the link: https://assets.ippc.int/static/media/files/publication/en/2016/03/A_Global_ePhyto_Feasibility_Study.pdf
Exchange of electronic Phytosanitary Certificates
More efficient certification process
Reduced fraud
Transparency
Korea itends to gradually extend implementation of Epyhto with a number of countries, including Generic ePhyto National System (GeNS) countries (Uganda, Sri Lanka and Guatemala).
Standards
Authentication of systems that contact the hub through X.509 certificates
Sender identity verified through X.509 certificates
Single Web Services Description Language (WSDL)
UN/CEFACT schema v12B
Exchange protocol is Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) over HTTPS
Retrieving messages from the hub will be through a push or pull method.
For more details refer to the link: https://www.ephytoexchange.org/landing/hub/index.html
https://www.ephytoexchange.org/landing/harmonization/index.html
https://www.ephytoexchange.org/landing/hub/index.html

