A. General Information
Pacific Alliance- Electronic exchange of customs information (Chile, Mexico,Peru,Columbia)
B. Lessons Learned
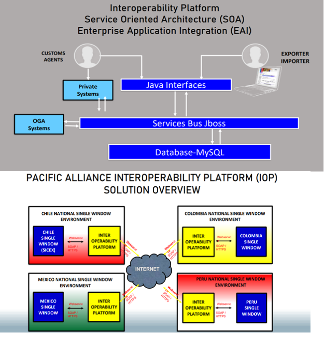
The Pacific Alliance interoperability project aims at connecting single windows of its four member states in line with international standards. It allows for exchanges of custom information.
The Pacific Alliance member countries established their single windows between 2006 and 2013, allowing economic operators to process permits and authorizations from a single website, and, in some cases, to pay fees for foreign trade operations. Single windows bring a series of benefits, including shorter processing times, lower costs, and less uncertainty. They also improve coordination and transparency among public entities.
To expand these benefits, the Pacific Alliance countries launched its interoperability project in 2016 with the goal of connecting its single windows and exchanging, in real time, the information contained in the main documents that accompany foreign trade operations. The Pacific Alliance countries began exchanging phytosanitary certificate data in 2017 and certificate of origin data in 2018.
The process involves bilateral point-to-point data exchanges, without going through a central body. This means that the model does not depend on a central coordinator, which makes it more sustainable and enables other countries in the region to join.
The need to make trade more sufficient, improve risk management procedures at border, and promote international standards.
Single windows are the only channel of interoperability for trade related documents on information delivered by parties.
Single Windows’ interoperability must secure secure the availability of documents and information in accordance with the operations’ conditions set forth by parties.
Each Single Window must exchange information with foreign trade systems as appropriate in its territory, to facilitate the entry and departure of goods.
Each SW must exchange information with foreign trade systems as appropriate in its territory, to facilitate the entry and departure of goods.
Electronic exchange of phytosanitary certificates
Electronic exchange of certificates of origin.
Exchange of phytosanitary certificates are based on UN model and standards.
Exchange of certificates of origin are based on WCO standards.
Technical, legal issues with regards to making single windows interoperable.
Costs for foreign trade procedures has been cut.
Processing time was reduced.
Waiting time to clear customs was cut.
Technical solution by software company(CrimsonLogic)
Support from IDB (Inter-American Development Bank)
The Pacific Alliance countries have set the goal of building on this solution by adding new certificates and documents to the program and including other strategic trade partners.
https://na.eventscloud.com/file_uploads/6dd12a66be0af3c06fd36e4d1f2b99d6_eduardogarciagodos.pdf
https://unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trade/agr/meetings/OtherMtgs/eQuality_June2020/e-Cert_Mexico_10_junio_2020.pdf

