A. General Information
1. Title
World’s first digital trade financing pilot between MLETR harmonised jurisdictions
2. Status of the project
Pilot
3. Implementation period of the project/service:
5. Geographical coverage
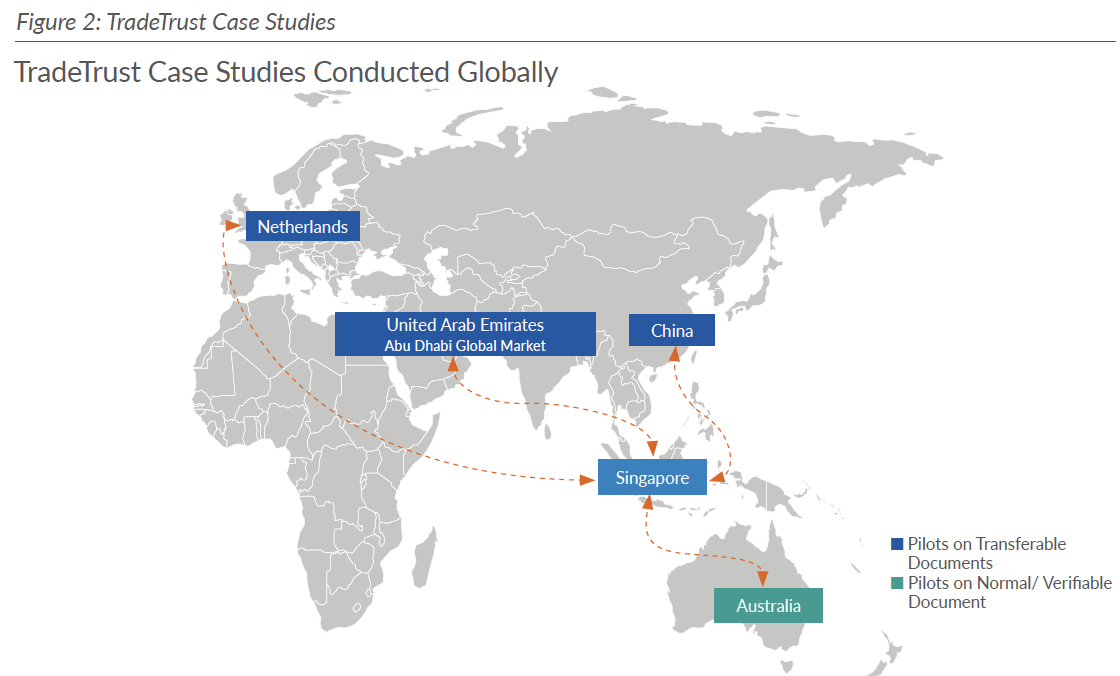
Bilateral
Participating countries: Singapore, United Arab Emirates
6. Participating agencies/entities of the project/service:
a. Development stage
Lead agencies/entities
IMDA, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
and the Financial Services Regulatory Authority
(FSRA) of Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM)
Other participating agencies/entities
--
b. Operational stage
Lead agencies/entities (op)
--
Other participating agencies/entities (op)
--
7. Main stakeholders/beneficiaries of the project
Traders (big enterprises)
Transport
Other Government Agencies (OGAs)
8. Business process category of the project
Commercial Transactions
Forwarding and cargo handling
Transport
Payment
B. Lessons Learned
9. Summary description of the project/service
Brief Summary
This pilot project aims to facilitate the transfer of electronic documents between jurisdictions that have adopted the UNCITRAL MLETR and to harmonize the legal recognition of digital documents, such as electronic bills of lading in the jurisdictions of Singapore and Abu Dhabi.
a. Objective(s)
IMDA, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) of Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), in collaboration with commercial partners, DBS Bank, Emirates NBD and Standard Chartered, have successfully concluded the world’s first cross-border digital trade financing pilot of its kind. The pilot announced in November 2021 used IMDA’s TradeTrust framework to facilitate the transfer of electronic records between jurisdictions that have adopted the UNCITRAL MLETR. This harmonizes the legal recognition of digital documents such as eBLs across both jurisdictions and complements the larger global trade movement by the G7 economies on adopting electronic transferable records in international trade.
b. Business need for the project (background)
Transferable documents: Trade documents that entitle the holder to claim the performance
of an obligation or ownership (e.g. bills of lading, bills of exchange, etc.). In 2017, The UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR) was introduced to enable legal use of transferable electronic records (ETRs) that are functionally equivalent to transferable documents. The ETRs would need to satisfy the requirements of singularity, exclusive control and integrity. Blockchain technology can be used in the implementation of ETRs. For example, the ERC721 provides a smart contract API used for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that supports transfers of ownership whilst being able to provide satisfaction of key functional requirements of the MLETR.
c. Business process covered*
--
d. Overall architecture and functionalities*
--
e. Relevant document/figure
10. Documents and data exchanged via the project
Electronic Bill of Lading, and others.
11. Data models/databases, proprietary solutions, hybrid approaches
--
12. Main challenges faced during the project
--
13. Lessons learned from the project
--
14. Main benefit(s) of the project
Transaction Cost savings*
Transaction Time savings
Simplified process
14A. Elaborations/detailed description on benefits gained
--
15. Technical/financial/capacity building/other assistance
--
16. Future plan for expansion of the project
--
17. Other information or relevant references on the project
--
18. Relevant document regarding the project
C. Relevant Standards
19. Name(s) of any international, national legal instrument underpinning the project
--
20. Electronic message standard
20A. Electronic message standard supporting the project
--
20B. Type of standard for electronic message applied for the project
21. Technical communication standard
21A. Technical communication standard supporting the project
--
21B. Type of technical communication standard applied for the project
22. Security-related standards*
22A. Security-related standard supporting the project
--
22B. Type of security-related standard applied for the project
--
23. Other Technical Information
23A. Interface developed for data exchange with an internal system
--
23B. Other technical implementation information
Blockchain Platforms