A. General Information
Digital FIATA Bill of Lading
B. Lessons Learned
The International Federation of Freight Forwarders Associations is now issuing digital bills of Lading though Transport Management Systems, on a global scale. Each document is registered on an immutable ledger and can be verified at any time by all stakeholders interacting with the document.
- Provide an easy access to digital FBL
- Allow freight-forwarders to issue FBL directly through their everyday tools (TMSs and other software)
- Strengthen the compliance around the FBL distribution
- Address fraud issues and strengthen document security and allow stakeholders to easily verify the validity of the document
Need to resolve the multiple challenges brought by the usage of paper trade documents:
- Cumbersome process prompt to errors
- Transport of paper document is long and costly, there is a risk of documents to be lost or documents arriving after the goods
- Risks of fraud and falsification of paper documents
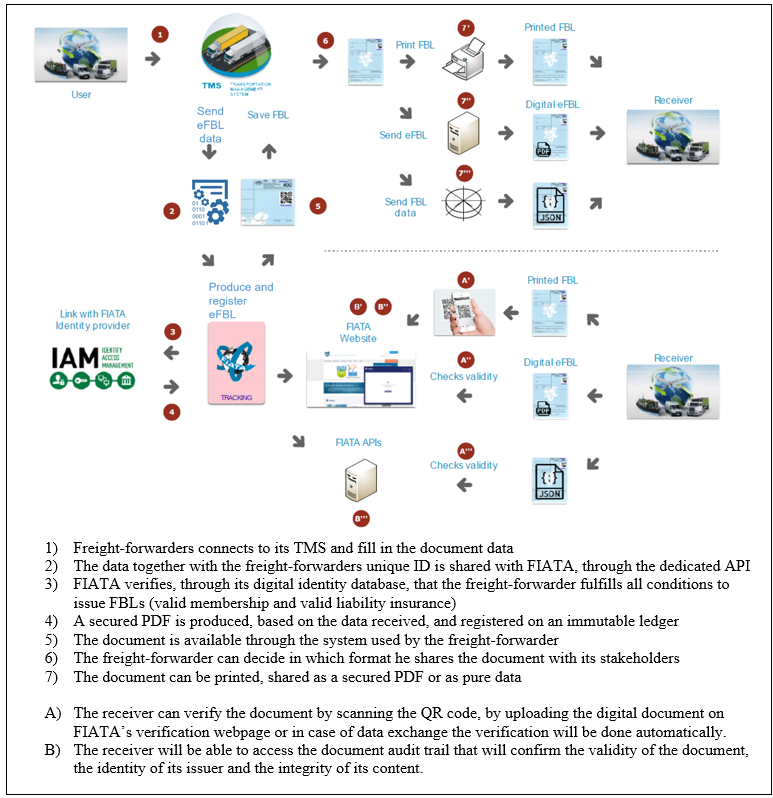
- Freight-forwarders issue digital FBL through their daily tools (TMS and other software).
- Freight-forwarders can decide in which format they share the document with their stakeholders (printed or digital).
- Stakeholders interacting with the document can verify it by scanning the QR code or uploading the document on FIATA’s verification webpage https://fiata.org/document-verification/
FIATA encourages all TMS’s, eBL providers and other software providers to join them and implement FIATA’s solution to offer this new service to their customers. All technical specifications are available on FIATA’s GitHub repository.
The solution, developed by FIATA partner Komgo, will help to reduce fraud risks, as each document is recorded on an immutable ledger and will be verifiable at any time by all stakeholders interacting with the document. Stakeholders will be able to either scan the QR code at the top right of the document, or directly upload the PDF on FIATA’s verification page to access the document audit trail which will
- Certify the validity of the document,
- The identity of its issuer,
- The integrity of its content.
The eFBL data standard includes all data elements required on the digital FBL. Technical specifications can be found on FIATA’s Git Hub repository: https://github.com/FIATA/eFBL
The eFBL data standard was created on the basis of the mapping of the paper FBL and the UNCEFACT MMT Reference data model, it is therefore fully aligned with this one.
The main lesson learned through this project is to keep things simple and not to try to solve all issues at once. We tried to keep a pragmatic approach during the whole development process and the solution itself is very pragmatic and flexible, as it allows our members to become digital freight-forwarders at their own rhythm. They can choose how far they want to go in the digitalization process.
There are several benefits for different parties:
For Freight-forwarders:
- Save time and money - Issue digital documents within seconds 24/7 and save money by avoiding costs generated by paper documents.
- Optimize your processes - Issue secured digital FBLs directly from your TMS and avoid double data entry.
- Bring trust and security - Give the possibility to your stakeholders to verify at any time: the validity of the eFBL, your identity as well as the document content integrity.
- Achieve your sustainability goals - Embrace a green solution, help saving paper and unnecessary courier services.
- Flexibility of format - Decide in which format you want to share your FBL with your stakeholders: in a digital format (PDF) or you can always print it if needed.
For stakeholders receiving the document:
- Additional trust and security: digital FBL can be verified at anytime and from anywhere
- Save time by having easy access to information needed
FIATA Association members:
- Less administrative tasks as the majority of the solution is handled centrally by FIATA
Komgo services have been/are used to develop and manage the technical solution. Forgerock identity management system is used as the backbone of FIATA’s digital identity registry.
The solution is currently being rolled out through FIATA’s associations members worldwide.
It is planned to be expanded to other FIATA standard documents such as the FIATA Forwarders Certificate of Receipt, FIATA Warehouse Receipt and the Non-negotiable FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill.
FIATA is exploring possibilities to enhance the solution to facilitate exchanges of relevant data with specific stakeholders, such as custom authorities, carriers and banks.
UN/CEFACT Multimodal Transport Reference Data Model